Dardanos Tumulus
- Location and Accessibility
- Architectural Features and Design
- Interior Chamber and Burials
- Historical Context and Importance
- Excavations and Discoveries
- Myths and Legends
- Cultural Significance and Heritage
- Visiting the Dardanos Tumulus: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Things to See and Do Nearby
- Photography and Videography
- Accessibility for Visitors with Disabilities
- Guided Tours and Local Guides
- Insider Tip: The Best Time to Visit
Location and Accessibility
The Dardanos Tumulus is situated in the historical Gallipoli Peninsula, within the borders of the modern-day city of Çanakkale in northwestern Turkey. The exact location of the tumulus is on the outskirts of the village of Beşiktepe, approximately 10 kilometers southwest of the city center.
To reach the Dardanos Tumulus, visitors can take a scenic drive or utilize public transportation. From Çanakkale, regular buses and minibuses depart for Beşiktepe, providing an affordable and convenient option. Upon arriving in Beşiktepe, a short walk or taxi ride will lead you to the tumulus site.
The Dardanos Tumulus is easily accessible from major cities and landmarks in the region. Çanakkale is well-connected by road, with direct routes to Istanbul, Bursa, and Izmir. The city also serves as a gateway to the Gallipoli Peninsula, where visitors can explore other historical sites related to the Trojan War.
Architectural Features and Design
The Dardanos Tumulus stands apart in terms of its unique architectural style, showcasing the ingenuity and craftsmanship of its ancient builders. Constructed using locally sourced materials, primarily limestone and granite, the tumulus exhibits a remarkable level of precision in its construction. Large stone blocks were carefully cut and fitted together without the use of mortar, creating a sturdy and imposing structure.
The tumulus, measuring approximately 60 meters in diameter and 12 meters in height, features a distinctive conical shape. Its imposing presence is further enhanced by the surrounding landscape, where it rises prominently against the backdrop of the rolling hills and the shimmering waters of the Dardanelles Strait.
The tumulus's interior chamber is accessed through a narrow passageway leading to a spacious burial chamber. This chamber, believed to be the final resting place of Dardanos or other significant individuals, is characterized by its impressive corbelled roof, a technique involving the gradual overlapping of stone blocks to form a self-supporting structure.
Interior Chamber and Burials
The Dardanos Tumulus contains a remarkable burial chamber, a testament to the elaborate funerary practices of ancient Anatolia. Excavations have revealed a spacious chamber constructed from large stone blocks, its walls lined with intricately carved reliefs depicting scenes from mythology and daily life.
Within the chamber, archaeologists have discovered the skeletal remains of several individuals, believed to be members of the ruling elite of ancient Troy. Accompanying the remains were a wealth of artifacts, including bronze weapons, gold jewelry, and ceramic vessels, offering glimpses into the material culture and craftsmanship of the period.
The identities of the individuals buried in the tumulus remain a subject of debate among scholars. Some theories suggest that the chamber served as the final resting place for Dardanos himself, the legendary founder of Troy, while others propose that it may have been used for multiple burials of prominent figures from the ruling dynasty.
The significance of these burials extends beyond the individuals interred within the tumulus. They provide valuable insights into the social structure, religious beliefs, and funerary practices of ancient Anatolian society, shedding light on the cultural and historical context of this remarkable site.
Historical Context and Importance
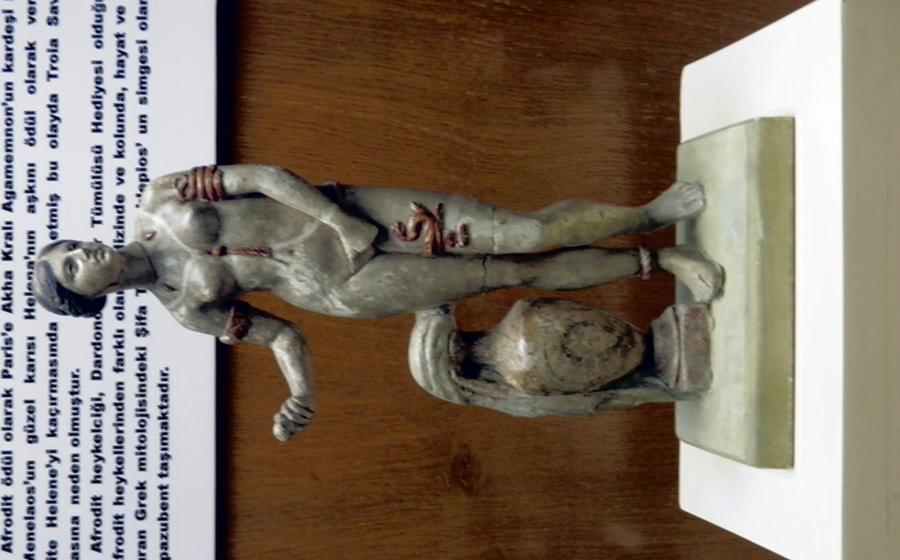
The Dardanos Tumulus holds immense historical significance, deeply intertwined with the ancient city of Troy and the legendary Trojan War. According to Greek mythology, Dardanos, the legendary founder of Troy, was buried beneath this very tumulus. His tomb became a symbol of the city's origin and a testament to its rich history.
The tumulus also plays a pivotal role in the Trojan War narrative. It is believed that the tumulus was located just outside the gates of Troy, serving as a poignant reminder of the city's vulnerability and the impending conflict. The tumulus thus became a powerful symbol of the Trojan people's struggle against the invading Greek forces.
Beyond its mythological associations, the Dardanos Tumulus holds significant cultural importance in ancient Anatolia. Tumuli, or burial mounds, were common throughout the region and served as monumental markers of power and prestige. The size and grandeur of the Dardanos Tumulus suggest that it belonged to a prominent individual, possibly a ruler or a high-ranking official.
The tumulus also provides valuable insights into ancient Anatolian burial practices and customs. The presence of a burial chamber within the mound, along with the discovery of human remains and artifacts, sheds light on the funerary rituals and beliefs of the ancient inhabitants of the region.
Overall, the Dardanos Tumulus is a treasure trove of historical and cultural significance, offering a glimpse into the ancient world of Troy, the Trojan War, and the broader context of Anatolian history.
Excavations and Discoveries
The Dardanos Tumulus has been the subject of several archaeological excavations over the years. The first systematic excavations were conducted in the 19th century by German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, who was also responsible for the discovery of the ancient city of Troy. Schliemann's excavations revealed the existence of a large burial chamber within the tumulus, as well as a number of artifacts, including pottery, jewelry, and weapons.
In the 20th century, further excavations were carried out by Turkish archaeologists, who uncovered additional human remains and artifacts. These excavations also revealed the complex construction techniques used in the construction of the tumulus, including the use of large stone blocks and a sophisticated system of drainage channels.
One of the most significant discoveries made during the excavations was the discovery of a gold diadem, or headband, which is believed to have belonged to Dardanos himself. The diadem is decorated with intricate designs and is considered a masterpiece of ancient craftsmanship.
Despite the extensive excavations that have been conducted, the Dardanos Tumulus still holds many secrets. Ongoing research and future excavations are expected to shed light on the construction, use, and significance of this ancient monument.
Myths and Legends
The Dardanos Tumulus is steeped in ancient Greek myths and legends, adding to its cultural significance and allure. According to mythology, Dardanos, the legendary founder of Troy, was the son of Zeus and Electra. He was said to have traveled from Arcadia in Greece to Anatolia, where he established the city of Dardania, which later became Troy. The tumulus is believed to be the burial mound of Dardanos, marking the origins of the Trojan civilization.
The Trojan War and the Tumulus
The Dardanos Tumulus is intricately linked to the epic tale of the Trojan War. In Greek mythology, Paris, the son of King Priam of Troy, abducted Helen, the wife of King Menelaus of Sparta. This sparked the Trojan War, a legendary conflict between the Greeks and Trojans. The tumulus is believed to have served as a vantage point for the Trojan elders to observe the unfolding battles on the plains below.
Interpretations and Retellings
Over the centuries, the myths and legends associated with the Dardanos Tumulus have been interpreted and retold in various forms. Ancient Greek poets, such as Homer and Virgil, immortalized these tales in their epic works, ensuring their enduring legacy. Modern retellings and adaptations of the Trojan War narrative continue to captivate audiences, keeping the myths alive and relevant.
Symbolism and Significance
The myths and legends surrounding the Dardanos Tumulus hold profound symbolism and significance. They reflect the ancient Greek belief in divine origins and the interconnectedness of gods and mortals. The tumulus represents the tangible link between the mythical past and the historical reality of Troy, blurring the lines between myth and history.
Exploring the Tumulus through Myths
Exploring the Dardanos Tumulus through the lens of ancient myths and legends offers a unique and immersive experience. Visitors can imagine themselves as characters in the epic Trojan War, standing atop the tumulus and witnessing the legendary battles unfold. The myths add a layer of depth and enchantment to the site, making it a truly captivating destination for history and mythology enthusiasts alike.
Cultural Significance and Heritage
The Dardanos Tumulus holds immense cultural significance as a symbol of Turkish heritage. Its connection to ancient Troy and the legendary figure of Dardanos has contributed to its enduring importance in Turkish history and mythology. The tumulus has become a symbol of national pride and identity, representing the deep cultural roots of the Turkish people.
In recent years, the Turkish government has recognized the importance of preserving and promoting the Dardanos Tumulus as a valuable cultural asset. The site has been designated as a protected archaeological area, and efforts have been made to restore and maintain its integrity. The government has also invested in cultural tourism initiatives to promote the tumulus and other historical landmarks in the region, attracting both domestic and international visitors.
Educational programs and initiatives have been developed to raise awareness about the cultural significance of the Dardanos Tumulus and its role in ancient Anatolian history. Schools and universities offer courses and workshops on the subject, and the site is frequently visited by students and researchers for educational purposes.
By preserving and promoting the Dardanos Tumulus, Turkey aims to ensure that this important cultural heritage site continues to be a source of pride and inspiration for future generations. The tumulus serves as a reminder of the region's rich history and the enduring legacy of ancient civilizations that have shaped the cultural tapestry of Turkey.
Visiting the Dardanos Tumulus: A Step-by-Step Guide
Planning Your Visit:
Research and Preparation: Before your trip, take some time to learn about the history, significance, and legends surrounding the Dardanos Tumulus. This will enhance your experience and appreciation of the site.
Transportation: The tumulus is easily accessible by car. If you're coming from Çanakkale, follow the signs towards Eceabat and then turn onto the road leading to the site. Parking is available nearby.
Entrance Fees: There is a small entrance fee to visit the Dardanos Tumulus. The fee helps support the preservation and maintenance of the site.
Exploring the Tumulus:
Exterior: Begin your visit by exploring the exterior of the tumulus. Admire its impressive size and unique architectural features. Take some time to walk around the base and capture photos from different angles.
Interior Chamber: If it's open to visitors, you can enter the burial chamber within the tumulus. Be prepared for a narrow and low passageway. Inside, you'll find an impressive domed chamber with stone walls.
Artifacts and Exhibits: While inside the chamber, take note of any artifacts or exhibits that may be on display. These items can provide valuable insights into the history and significance of the tumulus.
Surroundings: After exploring the tumulus, take some time to walk around the surrounding area. You'll find yourself amidst a tranquil landscape with stunning views of the Dardanelles.
Tips for a Fulfilling Visit:
-
Duration: Plan to spend at least an hour exploring the Dardanos Tumulus. This will give you enough time to take in its history, admire its architecture, and wander around the surroundings.
-
Weather: Choose a clear day for your visit to fully appreciate the views and the surrounding landscape.
-
Photography: Bring a camera to capture the beauty of the tumulus and its surroundings. Just be sure to follow any photography guidelines or restrictions that may be in place.
-
Respect: Remember that the Dardanos Tumulus is a sacred and historic site. Be respectful of the site and its significance, and avoid any actions that could damage or disturb it.
Things to See and Do Nearby
In addition to exploring the Dardanos Tumulus, visitors can immerse themselves in the rich history and natural beauty of the surrounding area. Just a short distance from the tumulus, history buffs can delve into the ancient world at the Troy Museum, which houses a fascinating collection of artifacts unearthed from the legendary city of Troy. Nature enthusiasts, on the other hand, will find solace in the picturesque Kilitbahir Nature Park, with its stunning views of the Dardanelles Strait. For those seeking a unique cultural experience, the nearby village of Ezine offers a glimpse into traditional Turkish life, with its charming streets, colorful markets, and delicious local cuisine.
Whether you're a history buff, nature lover, or simply seeking a unique cultural experience, the area surrounding the Dardanos Tumulus promises an unforgettable journey through time and tradition. With its rich tapestry of attractions, from ancient ruins to natural wonders, this region offers something for every traveler.
Photography and Videography
The Dardanos Tumulus offers a stunning backdrop for capturing memorable photos and videos. Whether you're an amateur photographer or a professional, here are some guidelines to help you make the most of your experience:
Respect the Site: Always remember that the Dardanos Tumulus is a historical and cultural landmark. Respect the site and its surroundings by refraining from touching or climbing on the tumulus.
Use Natural Light: The best time to capture the tumulus is during the golden hours of sunrise and sunset, when the warm light enhances the texture and colors of the stone.
Experiment with Different Angles: Explore different angles to find unique perspectives of the tumulus. Take shots from a distance to capture its grandeur, and also get close-up shots to highlight its intricate details.
Consider a Tripod: A tripod will help you stabilize your camera and capture sharp, blur-free images, especially in low-light conditions.
Capture the Surroundings: Don't just focus on the tumulus itself. Take the opportunity to capture the surrounding landscape, including the nearby fields, hills, and sea.
Follow Regulations: Be aware of any regulations or restrictions regarding photography and videography at the site. Obtain the necessary permits if required.
Share Your Experience: Share your photos and videos with friends, family, and online communities. Use social media platforms to connect with other travelers and share your experiences at the Dardanos Tumulus.
Accessibility for Visitors with Disabilities
The Dardanos Tumulus is committed to ensuring that all visitors, including those with disabilities, have an enjoyable and accessible experience. Wheelchair accessibility is a top priority, with ramps and designated parking spaces available for easy access to the site. Visitors with disabilities can also request special arrangements or assistance, such as guided tours tailored to their specific needs. The staff is dedicated to providing a welcoming and inclusive environment for all, ensuring that everyone can explore and appreciate the historical and cultural significance of the Dardanos Tumulus.
Guided Tours and Local Guides
For those seeking a deeper understanding of the Dardanos Tumulus and its historical significance, guided tours are highly recommended. These tours, led by knowledgeable local guides, provide insightful commentary and anecdotes that bring the site to life.
One can find guided tours offered by various tour operators and local agencies. It is advisable to research and compare different options to find a tour that suits your interests and budget. Online platforms and travel agencies often provide detailed information about available tours, including schedules, prices, and itineraries.
Booking a guided tour in advance is recommended to secure your spot, especially during peak tourist season. When choosing a guide, it is essential to consider their experience, qualifications, and language proficiency. A good guide will not only share historical facts but also create an engaging and interactive experience for visitors.
With a knowledgeable guide, you can delve into the rich history of the Dardanos Tumulus, learn about the legends and myths surrounding it, and gain a deeper appreciation for its cultural significance. Guided tours offer a personalized and immersive way to explore this ancient site and make your visit truly memorable.
Insider Tip: The Best Time to Visit
Timing is everything when it comes to experiencing the Dardanos Tumulus at its best. To avoid the scorching summer heat and large crowds, plan your visit during the shoulder seasons of spring (April-May) or autumn (September-October). These months offer pleasant temperatures, fewer tourists, and a chance to witness the surrounding landscapes in their full bloom or vibrant autumn colors.
If you're a photographer or simply want to capture the most stunning shots of the tumulus, aim to visit during the golden hours of sunrise or sunset. The warm, diffused light casts a magical glow on the ancient structure, creating an ethereal atmosphere that's perfect for capturing unforgettable photographs.
Remember, the Dardanos Tumulus is a historical site, so it's essential to be respectful and mindful of your surroundings. Avoid making excessive noise or disturbing the tranquility of the area. Embrace the opportunity to connect with the past and immerse yourself in the rich history and cultural significance of this ancient wonder.