İnandık Village Ancient Phrygian Ruins
- The Ancient City of İnandık
- Location and Accessibility
- Excavations and Findings
- The Phrygian People
- Exploring the Ruins
- City Walls and Gates
- Acropolis and Temple
- Agora and Marketplace
- Necropolis and Tombs
- Rock-Cut Structures:
- Historical Significance
- Natural Surroundings
- Local Cuisine
- Cultural Experiences
- Insider Tip:
The Ancient City of İnandık
Historical significance: İnandık, an ancient city located in the Çankırı province of Turkey, holds significant historical importance as a testament to the Phrygian civilization that once flourished in Anatolia. Excavations at the site have revealed a wealth of artifacts and architectural remains, shedding light on the history, culture, and daily life of this enigmatic civilization.
Phrygian origins: The Phrygians, an Indo-European people, migrated to Anatolia from the Balkans around the 12th century BCE. They established a powerful kingdom that spanned much of central and western Anatolia, with Gordion as their capital. The Phrygians were renowned for their advanced metalworking skills, particularly in bronze, and their sophisticated art and architecture.
Architectural remains: At İnandık, visitors can explore the remnants of this ancient Phrygian city, which include impressive fortifications, temples, an agora, and a necropolis. The city walls, constructed from massive blocks of stone, once protected the settlement from invaders. The remains of a monumental temple complex, located in the acropolis, hint at the religious significance of the site.
Location and Accessibility
İnandık, an ancient city of Phrygian origin, is situated in the Central Anatolian region of Turkey. It is conveniently located in the Çankırı province, making it an easily accessible destination for history enthusiasts and travelers alike.
To reach İnandık, one can take various transportation options. The nearest airport is Çankırı Airport, which offers domestic flights from major cities in Turkey. From the airport, visitors can hire a car or take a taxi to cover the remaining distance to İnandık, which is approximately 30 kilometers.
Alternatively, travelers can opt for public transportation by taking a bus from Çankırı city center to İnandık. Buses depart regularly from the main bus station and offer a budget-friendly option for reaching the ancient city. The journey takes approximately 45 minutes, providing a scenic ride through the picturesque countryside.
Upon arrival in İnandık, visitors can explore the ancient ruins on foot. The site is relatively compact, allowing for easy navigation and exploration of the various structures and landmarks.
Excavations and Findings
Extensive excavations have been conducted at the ancient city of İnandık, revealing the rich cultural heritage of the Phrygian civilization. Archaeologists have uncovered a treasure trove of artifacts, including pottery, tools, jewelry, and inscriptions. These findings provide valuable insights into the daily lives, customs, and artistic traditions of the Phrygian people.
The ongoing archaeological work at İnandık has contributed significantly to our understanding of Phrygian culture and its place in ancient Anatolia. By piecing together the excavated artifacts and architectural remains, researchers are gaining a deeper comprehension of the city's layout, its social and economic structures, and its interactions with neighboring civilizations.
The discoveries at İnandık have also shed light on the Phrygian language, which was distinct from other Indo-European languages spoken in the region. Inscriptions found at the site have provided crucial information for deciphering the Phrygian script and understanding the unique linguistic characteristics of this ancient civilization.
The Phrygian People
The Phrygians were an ancient civilization that flourished in Anatolia, the region that now encompasses modern-day Turkey. Their origins are still debated, with some scholars suggesting a Balkanic or Central Asian ancestry. The Phrygians spoke an Indo-European language, closely related to Greek and Armenian, and developed a unique culture that influenced the region for centuries.
The Phrygians were skilled metalworkers, and their bronze and iron artifacts were highly prized throughout the ancient world. They were also accomplished weavers, and their textiles were renowned for their intricate designs and vibrant colors. In addition to their material culture, the Phrygians had a rich religious and mythological tradition, centered around the worship of the mother goddess Cybele and her consort Attis.
The Phrygians were a powerful and influential people, and their kingdom reached its peak in the 8th century BC. However, their power declined in the following centuries, and they were eventually conquered by the Persians in the 6th century BC. Despite their political demise, the Phrygian culture continued to exert a strong influence on the region, and their legacy can still be seen in the art, architecture, and customs of modern-day Turkey.
The Phrygians were a fascinating and complex people, and their history is still being studied and debated today. Their legacy continues to inspire and intrigue, and their ancient city of İnandık stands as a testament to their enduring influence.
Exploring the Ruins
A visit to the ancient city of İnandık offers a unique opportunity to explore the remnants of a once-thriving Phrygian settlement. As you wander through the site, you can marvel at the architectural remains that have stood the test of time, transporting you back to a bygone era.
Start your exploration by following the clearly marked paths that lead you through the ruins. Admire the remnants of houses, workshops, and other structures that once formed the bustling streets of İnandık. Take your time to examine the intricate stonework and carvings that adorn the buildings, offering glimpses into the artistic and cultural achievements of the Phrygians.
One of the highlights of the site is the well-preserved city gate, which served as the main entrance to İnandık. Imagine the hustle and bustle of people and trade as you step through the gate, picturing the daily life of the ancient inhabitants.
As you continue your exploration, you'll come across the remains of the city's acropolis, which was the religious and administrative center. Here, you can admire the foundations of the temple complex, where the Phrygians once worshipped their gods and goddesses.
Don't miss the opportunity to visit the agora, the commercial and social hub of İnandık. Here, you can envision the lively atmosphere as merchants displayed their goods and locals gathered to trade and socialize.
Remember to bring your camera to capture the essence of this ancient city. Every corner of İnandık holds a story waiting to be told, and your photographs will serve as lasting mementos of your journey through time.
City Walls and Gates
The ancient city of İnandık was surrounded by sturdy city walls, providing protection and defense against potential threats. These fortifications, constructed with large stone blocks, served as a barrier against invaders and ensured the safety of the inhabitants.
The gates of İnandık were strategically positioned along the city walls, allowing for controlled access and egress. These gateways were often heavily fortified, with towers and additional defensive structures to deter unwanted entries. The gates also played a vital role in regulating trade and facilitating communication with neighboring settlements.
Today, visitors to İnandık can explore the remains of the city walls and gates, which offer a glimpse into the defensive strategies and architectural prowess of the ancient Phrygians. These structures stand as testaments to the city's resilience and its ability to withstand external threats.
Acropolis and Temple
The acropolis, situated at the heart of İnandık, served as the city's religious and administrative center. Excavations have revealed the remains of an impressive temple complex, offering a glimpse into the religious practices of the Phrygians. The temple, once adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures, stood as a testament to the city's devotion to its deities. Visitors can explore the ruins of the temple, marveling at the architectural details that have survived the passage of time. The acropolis area also provides panoramic views of the surrounding landscape, allowing visitors to appreciate the strategic location of the ancient city.
Agora and Marketplace
The agora, or marketplace, was the bustling center of commerce and social interaction in the ancient city of İnandık. Here, locals and traders from neighboring regions gathered to buy and sell goods, exchange news, and conduct business. The agora was a vibrant hub of activity, filled with the sounds of haggling merchants, the laughter of customers, and the clatter of coins.
Excavations have revealed the remains of numerous shops and market stalls that once lined the agora. These structures were typically small, with open fronts and counters for displaying merchandise. Archaeologists have discovered a wide variety of artifacts in these shops, including pottery, metalwork, jewelry, and textiles. These finds provide valuable insights into the types of goods that were traded in İnandık and the daily lives of its inhabitants.
The agora was not just a place of commerce, but also a social gathering place. Here, people met to discuss the latest news, share stories, and catch up with friends. The agora was also the site of public events, such as festivals, religious ceremonies, and political gatherings. It was a place where the community came together to celebrate, mourn, and make important decisions.
Exploring the agora of İnandık is a fascinating experience that allows visitors to step back in time and imagine the bustling atmosphere of this ancient marketplace. As you wander among the ruins of the shops and stalls, you can almost hear the voices of the merchants and the laughter of the customers. The agora is a reminder of the vibrant and cosmopolitan nature of ancient Phrygian society.
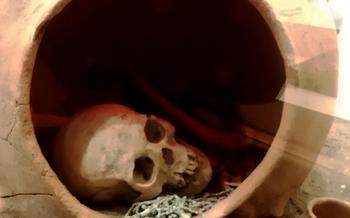
Necropolis and Tombs
The necropolis, or burial ground, of İnandık offers a fascinating glimpse into the funerary practices of the Phrygian people. Located outside the city walls, the necropolis contains a variety of tomb types, each reflecting the social status and wealth of the deceased.
One of the most common types of tombs at İnandık is the chamber tomb. These tombs are typically carved into the soft rock and consist of a single chamber, or sometimes multiple chambers, arranged around a central courtyard. The chambers were used to house the bodies of the deceased, along with their grave goods, such as jewelry, pottery, and weapons.
Another type of tomb found at İnandık is the tumulus. These tombs are large, earthen mounds that were built over the graves of important individuals. The tumuli were often surrounded by a circular stone wall, and sometimes they were topped with a stele, or carved stone marker, that bore the name of the deceased.
The necropolis at İnandık is an important source of information about Phrygian funerary customs. The variety of tomb types and the grave goods found within them provide valuable insights into the social structure, religious beliefs, and artistic traditions of this ancient civilization.
Rock-Cut Structures:
Among the most intriguing features of İnandık are its remarkable rock-cut structures. These architectural marvels are carved directly into natural rock formations, showcasing the ingenuity and craftsmanship of the Phrygians. While the exact purpose of these structures remains a subject of debate, they are believed to have served various functions, including as tombs, storage chambers, and even as living spaces.
These rock-cut structures are not only visually striking but also provide valuable insights into the daily lives and beliefs of the Phrygians. The intricate carvings and inscriptions found within these spaces offer glimpses into their religious practices, artistic traditions, and social customs. Visitors can marvel at the well-preserved carvings depicting scenes from mythology, daily life, and religious rituals.
Exploring these rock-cut structures is a truly unique experience that allows visitors to connect with the past in a tangible way. As you wander through these ancient chambers, you can almost feel the presence of the Phrygians who once inhabited this land. The atmosphere is palpable, transporting you back in time to a world long gone.
Historical Significance
İnandık's historical significance stems from its role as a prominent Phrygian settlement. Its strategic location allowed it to serve as a vital node in the Phrygian trade network, connecting the region to other major centers of Anatolia. Furthermore, İnandık played a crucial role in the defense of the Phrygian kingdom, with its fortified walls and strategic position acting as a bulwark against potential invaders. The city's decline and eventual abandonment coincided with the fall of the Phrygian kingdom, leaving behind a wealth of ruins that offer a glimpse into the culture and civilization of this ancient people.
The ruins of İnandık have been instrumental in shedding light on the broader history of the Phrygians. Excavations have uncovered a wealth of artifacts, including inscriptions, pottery, and other objects that have provided valuable insights into the daily lives, customs, and beliefs of this enigmatic civilization. By studying the remains of İnandık, archaeologists have been able to piece together the puzzle of Phrygian history, revealing their origins, their interactions with neighboring cultures, and their eventual demise.
Natural Surroundings
İnandık is nestled amidst a picturesque landscape of rolling hills and verdant valleys. The ancient ruins stand in harmony with the natural beauty, creating a serene and evocative atmosphere. Visitors can embark on leisurely nature walks through the surrounding countryside, immersing themselves in the tranquility of the Turkish countryside. The fresh air, vibrant greenery, and panoramic views offer a rejuvenating experience, complementing the historical exploration of the ancient city. Whether you seek a moment of contemplation or an invigorating hike, the natural surroundings of İnandık provide a welcome respite from the urban hustle and bustle.
Local Cuisine
When exploring the ancient ruins of İnandık, don't miss the opportunity to savor the delectable local cuisine. Çankırı, the province where İnandık is situated, boasts a rich culinary heritage influenced by both Turkish and Central Anatolian traditions. Indulge in mouthwatering kebabs, tender gözleme, and keşkek, a hearty dish made from bulgur and meat. Sample the region's famous mantı, delicate dumplings filled with minced meat and topped with yogurt and garlic sauce. For a sweet treat, try the local höşmerim, a delectable dessert made from shredded wheat and syrup. Supporting local businesses by dining at traditional restaurants or purchasing local products not only enriches your culinary experience but also contributes to the preservation of the region's culinary heritage.
Cultural Experiences
İnandık offers a unique opportunity to immerse yourself in the rich cultural heritage of the region. Engage with local customs and traditions by visiting traditional villages, interacting with friendly locals, and learning about their way of life. Attend cultural events and festivals that showcase the vibrant traditions of the region, such as traditional dance performances, music concerts, and local fairs. Explore local handicrafts and artisanal products, such as handwoven carpets, pottery, and jewelry, to gain deeper insights into the region's artistic expressions. By embracing these cultural experiences, you'll not only gain a deeper appreciation for the local culture but also contribute to the preservation of these traditions for future generations.
Insider Tip:
To fully immerse yourself in the ancient world of İnandık, consider visiting the site during the off-season. The absence of large crowds allows you to appreciate the ruins at your own pace, soak in the tranquility, and capture stunning photographs without distractions.
Combine your visit to İnandık with other nearby attractions for a comprehensive historical and cultural experience. The region is home to several other ancient sites, including Gordion, the capital of Phrygia, and the Hattusha, the capital of the Hittite Empire.
Enrich your exploration of İnandık by hiring a local guide. These knowledgeable individuals can provide in-depth insights into the history, culture, and significance of the site. Their expertise will transform your visit into a truly immersive and educational experience.