Alacahöyük a significant archaeological site
- Unveiling Alacahöyük: A Journey Through History
- A Majestic Citadel: The Mound of Alacahöyük
- Unraveling the Secrets: Excavations and Discoveries
- The Sphinx Gate: A Symbol of Power and Prestige
- The Alacahöyük Museum: A Treasure Trove of Discoveries
- Exploring the Environs: Çorum's Hidden Gems
- Unveiling the World of the Hittites: Alacahöyük's Historical Context
- The Art of the Hittites: Masterpieces from Alacahöyük
- The Hittite Language: Deciphering an Ancient Script
- Alacahöyük in Popular Culture: Beyond Archaeology
- Ethical Considerations in Archaeological Research
- Sustainable Tourism Practices at Alacahöyük
- Alacahöyük and the Future: Ongoing Research and Developments
- Insider Tip: Capturing the Magic of Alacahöyük
Unveiling Alacahöyük: A Journey Through History
Alacahöyük, a significant archaeological site located in the province of Çorum, Turkey, offers a captivating glimpse into the rich history and cultural heritage of ancient Anatolia. Its strategic position on the trade routes between Mesopotamia and the Caucasus made it a crucial hub for cultural exchange and interaction. Excavations at Alacahöyük have unearthed remarkable artifacts and structures, providing valuable insights into the development of ancient civilizations in the region.
The site's historical significance lies in its association with the Hattians, Hittites, and Phrygians, who successively inhabited the area. The Hattians, the earliest known inhabitants, laid the foundation for the region's cultural development. The Hittites, who rose to prominence in the 17th century BCE, transformed Alacahöyük into a major administrative and religious center. Their reign left an indelible mark on the site, with the construction of impressive fortifications, temples, and royal tombs. The Phrygians, who succeeded the Hittites, further contributed to the site's cultural and historical legacy.
Alacahöyük's discoveries have played a pivotal role in understanding the development of ancient Anatolian civilizations. The excavation of royal tombs, adorned with exquisite gold artifacts, has shed light on the wealth and power of the Hittite rulers. The decipherment of Hittite cuneiform tablets has provided invaluable information about their language, history, and religious beliefs. These discoveries have revolutionized our understanding of the ancient Near East and established Alacahöyük as a crucial site for archaeological research.
Currently, Alacahöyük remains an active archaeological site with ongoing excavations and research projects. Archaeologists continue to uncover new artifacts and structures, further enriching our knowledge of this ancient city. Alacahöyük stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of the civilizations that once flourished in Anatolia, inviting visitors to embark on a journey through time to explore its captivating history and cultural significance.
A Majestic Citadel: The Mound of Alacahöyük
The mound of Alacahöyük stands as a testament to the ingenuity and grandeur of ancient civilizations. Rising prominently from the surrounding landscape, this artificial elevation conceals a wealth of architectural wonders that reveal the sophistication and power of its former inhabitants.
Encircled by imposing defensive structures, the mound served as a formidable citadel, protecting its inhabitants from external threats. These fortifications, constructed with meticulous precision, showcase the advanced engineering skills of the time. Massive walls, reinforced with towers and gateways, formed an impenetrable barrier, ensuring the security and autonomy of the settlement.
Within the fortified walls, the Royal Palace and administrative buildings stood as symbols of authority and governance. These grand structures, adorned with intricate carvings and vibrant murals, housed the rulers and their court, who exercised their power and influence over the surrounding regions.
The religious significance of the mound is evident in the presence of numerous temples and shrines. These sacred spaces, dedicated to various deities, served as centers of worship and ritual practices, fostering a deep connection between the inhabitants and their spiritual beliefs. The discovery of elaborate altars, votive offerings, and religious artifacts provides valuable insights into the spiritual life of this ancient community.
Unraveling the Secrets: Excavations and Discoveries
The first excavations at Alacahöyük were conducted in the early 20th century by Turkish archaeologist Hamit Zübeyr Koşay. These excavations revealed a wealth of artifacts and structures, including the impressive Sphinx Gate and the royal tombs. Koşay's work laid the foundation for subsequent excavations, which have continued to shed light on the rich history and culture of the site.
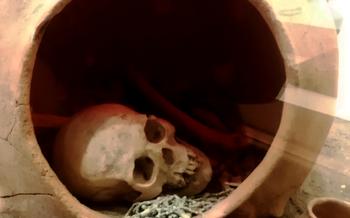
One of the most significant discoveries at Alacahöyük was the Royal Tombs, which contained elaborate burial chambers and a treasure trove of artifacts, including gold jewelry, bronze weapons, and ceramic vessels. These tombs provided valuable insights into the funerary practices and beliefs of the ancient Hittites. The artifacts also helped scholars to understand the extent of Hittite trade and cultural exchange with other civilizations in the region.
Another important discovery was the Sphinx Gate, which is considered one of the most iconic landmarks of Alacahöyük. The gate is decorated with two large sphinx sculptures, which are believed to represent the Hittite gods. The Sphinx Gate was likely used for ceremonial purposes and served as an entrance to the royal palace.
The excavations at Alacahöyük have also yielded a wealth of other artifacts, including pottery, tools, weapons, and seals. These artifacts have helped archaeologists to piece together the daily lives of the ancient Hittites and to understand their cultural and technological development.
The Sphinx Gate: A Symbol of Power and Prestige
The Sphinx Gate at Alacahöyük stands as a testament to the Hittites' architectural prowess and cultural significance. This monumental gateway, constructed from massive stone blocks, features a pair of imposing sphinxes flanking a central passageway. The sphinxes, carved with meticulous detail, display human heads adorned with elaborate headdresses, as well as lion-like bodies and wings.
The gate's symbolism is deeply rooted in Hittite mythology and iconography. The sphinxes represent protective deities, often associated with the Hittite goddess Inara, who was believed to guard the realm of the gods and ensure the prosperity of the kingdom. The gate's placement at the entrance to the city suggests its role as a symbolic barrier, protecting Alacahöyük from external threats and marking the transition from the mundane world to the sacred realm of the Hittite rulers.
During ancient times, the Sphinx Gate served as a grand entrance for ceremonial processions and religious rituals. It is believed that the Hittite kings and their entourage would pass through the gate on special occasions, such as religious festivals or military victories, to seek blessings and protection from the gods.
Comparisons can be drawn between the Alacahöyük Sphinx Gate and other sphinx representations in the ancient Near East. Similar structures have been found at sites such as Hattusa, the Hittite capital city, and Emar, an important trading center in northern Syria. These sphinxes share common features, such as the human-headed, lion-bodied form and the association with protective deities. However, each gate exhibits unique artistic interpretations and variations in style, reflecting the diverse cultural influences within the ancient Near East.
The Alacahöyük Museum: A Treasure Trove of Discoveries
The Alacahöyük Museum, situated in close proximity to the archaeological site, serves as a repository for the remarkable artifacts unearthed during excavations. This treasure trove of discoveries offers visitors an immersive journey into the rich history of Alacahöyük and its inhabitants.
The museum's collection encompasses a diverse array of artifacts, including exquisite jewelry, intricately carved stone tablets, bronze weapons, and pottery adorned with captivating motifs. Among the highlights are the iconic gold and silver vessels, which showcase the exceptional craftsmanship of the ancient artisans. These artifacts provide valuable insights into the artistic traditions, technological prowess, and cultural practices of the Hittites and their contemporaries.
Interactive displays and educational programs at the museum further enhance the visitor experience, bringing the ancient world to life. Informative panels, multimedia presentations, and hands-on exhibits provide a deeper understanding of the site's history, archaeological methods, and the significance of the discoveries.
Practical information for visitors includes the museum's location on Alacahöyük Caddesi in Çorum, its operating hours (generally from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM, closed on Mondays), and admission fees (which are quite reasonable and offer discounts for students and groups).
A visit to the Alacahöyük Museum is an essential complement to exploring the archaeological site itself. It allows visitors to appreciate the tangible remains of ancient civilizations, gain insights into their daily lives, and marvel at the enduring legacy of their cultural achievements.
Exploring the Environs: Çorum's Hidden Gems
Beyond the captivating allure of Alacahöyük, Çorum unveils a treasure trove of hidden gems that beckon adventurous travelers. Immerse yourself in the rich history and cultural heritage of the region by exploring nearby historical sites and museums. Marvel at the architectural wonders of ancient mosques and churches, each narrating tales of past civilizations. Discover the hidden wonders of natural landscapes, from cascading waterfalls to lush forests, offering a tranquil escape into nature's embrace.
Indulge in the delectable flavors of local cuisine, tantalizing your taste buds with traditional dishes that showcase the region's culinary prowess. Savor the warmth and hospitality of Çorum's people as you engage with the local community, learning about their customs and traditions. Craft a well-rounded itinerary that seamlessly blends history, nature, and culture, ensuring an unforgettable journey through Çorum's hidden treasures.
Unveiling the World of the Hittites: Alacahöyük's Historical Context
Alacahöyük stands as a testament to the grandeur and complexity of the ancient Hittite civilization. The Hittites emerged as a powerful force in Anatolia around the 17th century BCE, establishing a vast empire that rivaled the likes of Egypt and Babylonia. Their influence extended across the region, reaching as far as Syria and Mesopotamia.
The Hittites were skilled warriors and administrators, renowned for their innovative military tactics and their ability to forge diplomatic alliances. Their empire was characterized by a sophisticated bureaucracy, advanced legal systems, and a rich cultural heritage.
Alacahöyük offers a glimpse into the Hittites' origins and their rise to power. Excavations at the site have uncovered evidence of early Hittite settlements dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE. Over time, Alacahöyük developed into a major political and religious center, serving as the capital of the Hittite kingdom during the Old Kingdom period (17th-16th centuries BCE).
The Hittites left behind a legacy of impressive architectural achievements, including monumental fortifications, palaces, and temples. They were also skilled craftsmen, producing exquisite works of art in gold, silver, and bronze. Their distinctive iconography, featuring deities, mythical creatures, and scenes of royal processions, provides valuable insights into their religious beliefs and cultural practices.
The Hittite civilization eventually declined and fell to the invading Sea Peoples around 1200 BCE. However, their influence continued to resonate in the region, shaping the cultural and political landscape of the ancient Near East. Alacahöyük stands as a powerful reminder of this once-mighty civilization, offering a glimpse into their remarkable history and enduring legacy.
The Art of the Hittites: Masterpieces from Alacahöyük
The Hittites were renowned for their distinctive artistic style, which showcased a blend of realism, symbolism, and intricate craftsmanship. Excavations at Alacahöyük have unearthed a treasure trove of Hittite artifacts that provide valuable insights into their artistic prowess. These findings include exquisitely crafted gold jewelry, finely carved stone reliefs, and impressive bronze sculptures.
Hittite art is characterized by its attention to detail and the use of bold, geometric forms. Common motifs include processions of deities, scenes of hunting and warfare, and intricate animal designs. The Hittites also excelled in metallurgy, producing intricate bronze vessels, weapons, and jewelry. Their metalworking skills are evident in the stunning gold artifacts discovered at Alacahöyük, such as the famous Golden Sun Disk.
The Alacahöyük findings have played a crucial role in shedding light on Hittite art and its significance in the context of ancient Near Eastern artistic traditions. The site has yielded some of the finest examples of Hittite craftsmanship, demonstrating their mastery of various artistic techniques and their unique artistic vision.
By studying the art of Alacahöyük, we gain a deeper understanding of Hittite culture, their religious beliefs, and their social and political structures. The artistic legacy of the Hittites continues to inspire and captivate, serving as a testament to their enduring influence on the art world of the ancient Near East.
The Hittite Language: Deciphering an Ancient Script
The Hittites, who once ruled over a vast empire in ancient Anatolia, left behind a rich legacy of written records. Their language, known as Hittite, was a member of the Indo-European language family, sharing similarities with languages such as Sanskrit, Greek, and Latin. However, its decipherment proved to be a formidable challenge for linguists and archaeologists.
In the early 20th century, a team of German archaeologists led by Hugo Winckler stumbled upon a cache of clay tablets at the site of Boğazkale, the capital of the Hittite Empire. These tablets were inscribed with cuneiform script, a writing system that was also used by other ancient civilizations in the Near East.
The task of deciphering the Hittite language fell upon a young Czech linguist named Bedřich Hrozný. Through painstaking analysis and comparison with other known languages, Hrozný was able to crack the code and reveal the secrets of the Hittite script. His groundbreaking work, published in 1917, opened up a new chapter in the study of ancient Anatolia and shed light on the history and culture of the Hittite civilization.
The decipherment of the Hittite language had a profound impact on our understanding of the ancient world. It allowed scholars to access a wealth of historical, religious, and literary texts, providing insights into the political, social, and economic structures of the Hittite Empire. These texts have also shed light on the interactions between the Hittites and their neighbors, including the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Assyrians.
Today, the study of the Hittite language continues to be an active field of research. Scholars are working to decipher new texts, refine our understanding of Hittite grammar and vocabulary, and explore the relationship between Hittite and other Indo-European languages. The ongoing research on the Hittite language is helping us to piece together the puzzle of ancient Anatolia and gain a deeper appreciation for the rich cultural heritage of the Hittites.
Alacahöyük in Popular Culture: Beyond Archaeology
Alacahöyük's significance extends beyond the realm of archaeology, capturing the imagination of artists, writers, and filmmakers. References to this ancient site can be found in various forms of popular culture, contributing to its recognition and promoting cultural heritage on a global scale.
One notable example is the novel "The Hittite Enigma" by bestselling author Clive Cussler. The book features Alacahöyük as a central setting, weaving a thrilling tale of adventure and archaeological discovery. Cussler's novel has introduced the site to a wide audience, piquing their curiosity and inspiring them to learn more about its captivating history.
In the realm of cinema, Alacahöyük has made its appearance in several documentaries and historical films. These productions often showcase the site's impressive remains, shedding light on the grandeur of the Hittite civilization. Documentaries such as "Alacahöyük: The Secrets of the Hittites" and "Treasures of the Ancient World: Alacahöyük" provide viewers with an immersive experience, allowing them to virtually explore the site and its remarkable discoveries.
Furthermore, Alacahöyük's iconic Sphinx Gate has become a symbol of Turkey's rich cultural heritage, frequently featured in promotional materials and tourism campaigns. Its striking appearance and enigmatic aura have captured the attention of artists and designers, inspiring creative interpretations in various mediums.
Alacahöyük's presence in popular culture not only raises awareness of its historical importance but also contributes to the preservation and promotion of cultural heritage. By capturing the public's imagination, these artistic representations encourage individuals to explore the site in person and delve deeper into the fascinating world of the Hittites.
Ethical Considerations in Archaeological Research
Archaeological research at Alacahöyük, like any other archaeological endeavor, is guided by ethical principles and considerations. Excavations, artifact handling, and interpretation must adhere to responsible and ethical practices.
One key principle is minimizing the disturbance and impact on the site's cultural heritage. Archaeologists carefully plan excavations to avoid unnecessary damage to archaeological deposits and features. They employ non-invasive techniques and prioritize the preservation of the site's integrity for future generations.
Transparency and stakeholder involvement are crucial. Archaeologists engage with local communities, authorities, and experts to ensure that research benefits the local population and respects their cultural heritage. They seek informed consent and involve stakeholders in decision-making processes related to the site's management and preservation.
Ethical considerations also extend to artifact handling and documentation. Archaeologists meticulously record and document artifacts, ensuring their proper conservation and storage. Artifacts are studied and analyzed in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of damage or loss.
Research teams are responsible for publishing their findings and making them accessible to the scientific community and the public. Open access to research data and results promotes transparency and enables further study and collaboration.
Ethical dilemmas can arise when balancing the need for research with the preservation of cultural heritage. For instance, the decision to excavate a particular area or artifact may have implications for its future preservation. Archaeologists carefully weigh the potential benefits of research against the risks to the site's integrity.
By adhering to ethical principles, archaeologists strive to conduct research that is responsible, respectful of cultural heritage, and beneficial to society.
Sustainable Tourism Practices at Alacahöyük
Alacahöyük, with its rich history and cultural significance, has become a popular destination for tourists and history enthusiasts. However, the increasing number of visitors poses challenges to the preservation and sustainability of the site. To address these concerns, various initiatives have been implemented to promote responsible and sustainable tourism practices.
One of the key priorities is to minimize the environmental impact of tourism. Measures have been taken to reduce waste generation, promote energy efficiency, and protect the natural surroundings of the site. Visitors are encouraged to respect the environment, dispose of waste properly, and avoid activities that could damage the fragile ecosystem.
Another important aspect of sustainable tourism at Alacahöyük is community engagement. Local communities have been involved in the development and implementation of tourism initiatives, ensuring that they benefit from the economic and social opportunities brought by tourism. Community-based tourism projects, such as guided tours led by local experts, not only provide visitors with a deeper understanding of the site's history but also create employment and income-generating opportunities for the local population.
To further enhance the sustainability of tourism at Alacahöyük, visitors are encouraged to adopt responsible behaviors. This includes respecting the site's rules and regulations, staying on designated paths to avoid damaging the archaeological remains, and refraining from touching or removing artifacts. By following these guidelines, visitors can contribute to the preservation of Alacahöyük for future generations while also enjoying a fulfilling and educational experience.
Alacahöyük and the Future: Ongoing Research and Developments
Alacahöyük continues to be a fertile ground for archaeological exploration, with ongoing research projects shedding new light on the site's rich history and cultural significance. Excavations continue to uncover new structures and artifacts, providing valuable insights into the lives and customs of the ancient Hittites.
Innovative technologies such as 3D scanning and drone photography are being employed to create detailed maps and models of the site, aiding in the documentation and preservation of its intricate features. Interdisciplinary approaches involving archaeologists, historians, and scientists from various fields contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of Alacahöyük's past.
However, preserving and managing the site for future generations pose significant challenges. Balancing the need for further research with the conservation of the fragile remains requires careful planning and collaboration among stakeholders. Sustainable tourism practices that minimize environmental impact and promote community engagement are crucial for ensuring the longevity of Alacahöyük's heritage.
International partnerships and collaborations play a vital role in advancing research and fostering knowledge-sharing. Collaborative projects with institutions from around the world bring fresh perspectives and expertise, contributing to a deeper understanding of the ancient world.
As Alacahöyük's story continues to unfold, it holds immense promise for future discoveries and insights into the captivating history of the Hittite civilization.
Insider Tip: Capturing the Magic of Alacahöyük
To fully immerse yourself in the magic of Alacahöyük, timing and preparation are key. The best time to visit is during the shoulder seasons, spring (April-May) and autumn (September-October), when the weather is pleasant and the crowds are smaller.
For photographers, the golden hours of sunrise and sunset offer the most dramatic lighting, casting a warm glow on the ancient ruins. A sturdy tripod and a wide-angle lens will help you capture the vastness of the site and the intricate details of the architecture.
Local guides and tour operators can provide invaluable insights into the history and significance of Alacahöyük, bringing the past to life. They can also guide you to lesser-known spots for unique perspectives and photo opportunities.
Before your visit, delve into the rich history of the Hittites and Alacahöyük through books, documentaries, and online resources. This knowledge will enhance your appreciation of the site and allow you to connect more deeply with its ancient stories.
Alacahöyük offers a profound journey through time, where history, culture, and nature converge. Embrace the opportunity to explore this remarkable site, immerse yourself in its captivating aura, and uncover the secrets of a civilization that once ruled over a vast empire.